What Is Connected Vehicle Technology and What Are the Use Cases
Cars were once purely mechanical creations. You turned the key, pressed the pedal, and hoped for the best. Fast forward to today, and vehicles are no longer just machines that move people from point A to point B. They are intelligent, data-driven systems that communicate, learn, and adapt. This transformation is driven by connected vehicle technology, one of the most influential innovations shaping the modern automotive landscape.
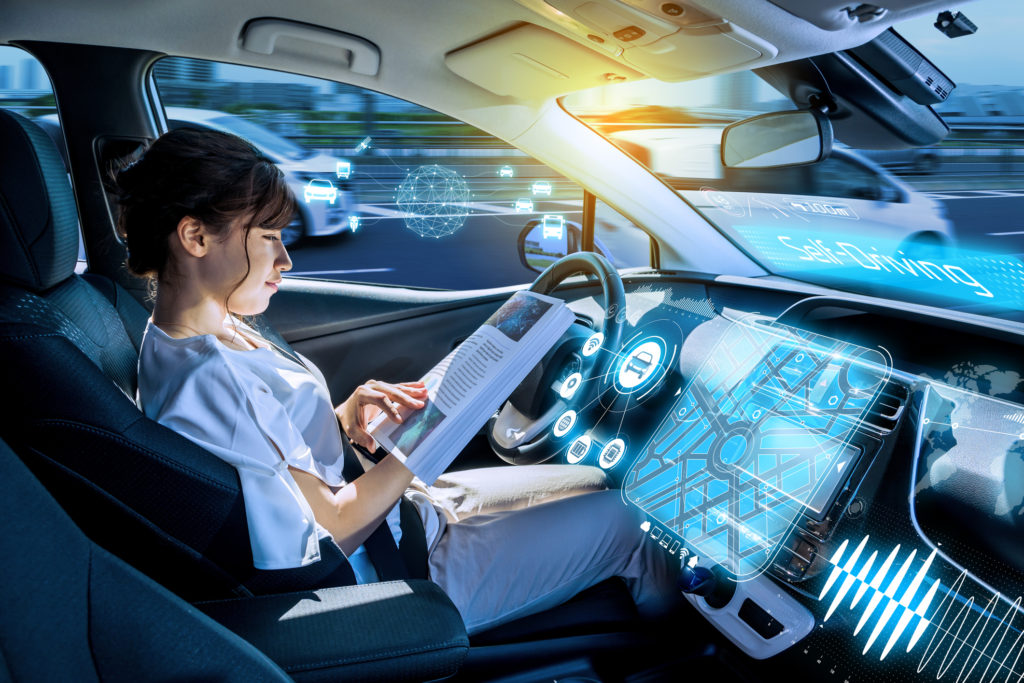
Connected vehicle technology answers the basic question of introducing the digital world into the driving experience. Cars are now able to communicate with other cars, roads, cloud systems, and even people. This stream of data allows for safer roads, easier traffic, more intelligent maintenance, and a more personal driving experience. Connected vehicles may be a future technology, but they are already present in our daily lives, and silently operate in the background every time you use your navigation application, get a service reminder, or listen to infotainment in the car.
Connected vehicles are gaining more and more importance as cities are becoming smarter, and mobility requirements are rising. They are the essence of higher driver assistance systems, intelligent transportation networks, and even autonomous vehicles. It is imperative to know what connected vehicles are and how they operate to gain a better understanding of the mobility of the future.
What Is a Connected Vehicle?
One of the questions that people usually ask is what a connected vehicle is. A connected vehicle is simply a car that is capable of communicating with external systems via the internet or wireless networks. Connected vehicles always communicate with their environment, as opposed to traditional vehicles that are solitary.
This connectivity enables the vehicle to transmit and receive information such as traffic, weather updates, road hazards, vehicle diagnostics, and software updates. Imagine that you are giving your car a voice and ears. It is able to listen to the surrounding world and react wisely.
Smart cars are based on hardware, software, and relationship technologies. Sensors receive the data, onboard systems analyze it, and communication modules send it to cloud servers or local infrastructure. The outcome is a car that is intelligent, receptive, and one that is constantly evolving.
Understanding Connected Vehicle Technology=
The technology that brings vehicles to communicate with the digital ecosystem around them is called connected vehicle technology. It integrates telecommunications, cloud computing, data analytics, and automotive engineering to become one integrated system.
To take one example, when a car on the road senses a sudden braking of the car in front, it could send out signals to other vehicles to reduce speed. This is because when there is congestion caused by traffic, the system will be able to propose alternative routes. When an element begins demonstrating the effects of wear, the driver is alerted to maintenance before the breakdown takes place.
Connected vehicle technology is not a feature but a platform that facilitates various applications. It is the basis of safety systems, infotainment systems, fleet management, and autonomous driving capabilities of the future.
Key Components of Connected Car Technology
Sensors and Embedded Hardware
Any networked automobile begins with hardware. Some of the sensors track engine performance and tire pressure, braking behavior, and the immediate environment. Cameras, radar, lidar, and ultrasonic sensors are rather important to collect real-time data.
These are the sensors that are similar to the senses of the vehicle. They listen, feel and see what is going on in and outside the car. Connected car technology will not work without proper sensor data.
Telematics Control Units (TCUs)
The Telematics Control Unit is the head of a connected vehicle. It deals with the interaction of the vehicle with other networks. TCUs deal with GPS, cell networks, and transmissions.
This element will make sure that the vehicle is not disconnected when the driver does not have their smartphone. It allows such vital services as emergency support, stolen cars, and remote diagnostics.
Communication Networks (V2V, V2I, V2X)
Con Vehicles make use of various communication models. Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) enables cars to communicate. Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) is an interface connecting vehicles and road systems and traffic lights. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) extends this communication down to pedestrians, networks, and devices.
Cloud Data Analytics and Cloud Platforms.
Intelligence in data is what cloud computing is concerned with. Cars transmit large volumes of data to cloud computers to be analyzed by sophisticated analytics and AI software.
This analysis assists manufacturers in advancing the performance of the vehicles, anticipating maintenance requirements, and enhancing user experiences. To the drivers, it translates to intelligent navigation, customized personalization, and constant upgrades.
In-car Infotainment Systems.
Connected car technology is most evident through infotainment systems. They offer navigation, entertainment, voice assistants, and smartphone integration.
Infotainment systems can be viewed as being convenience-centered, but they contribute to safety by minimizing distractions and sending real-time notifications.
How Connected Vehicles Work
Connected vehicles work cyclically: sense, communicate, analyze, and respond. The sensors gather information regarding the car and the environment. This information is carried via safe networks to cloud computing or local infrastructure.
After an analysis, the insights are relayed back to the vehicle or shared with other road users. All this occurs within milliseconds, which makes it possible to make decisions in real-time.
This process is improved through the introduction of IoT and AI. IoT is a connection that is flawless, and AI is an interpretation of complicated patterns of data. Collectively, they enable interconnected vehicles to predict problems instead of merely responding to them.
Vehicle Connectivity
- Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) Communication
V2V communication enables cars to exchange data like speed, direction, and braking status. This will avoid collisions, particularly when there is low visibility among drivers.
- Vehicle to Infrastructure (V2I) Communication
V2I links cars to traffic lights, road signs, and parking systems. It facilitates the smooth flow of traffic and minimizes traffic congestion.
- Vehicle to Cloud (V2C) Communication
V2C connectivity enables automobiles to have access to services on the clouds including navigation updates, diagnostics, and entertainment.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Ecosystem
V2X is the entire connectivity ecosystem, which entails bringing all forms of communication together into a system.
The Advantages of Connected Vehicle Technology
- Better Safety and Accident Prevention
Connected vehicle systems are one of the greatest advantages in terms of safety. Collision warnings, emergency response systems, and real-time alerts go a long way in decreasing the dangers of an accident.
- Better Driving Experience
Self-driving cars provide individualized experiences, including favorite routes, personalized infotainment, and so on.
- Vehicle Health and Predictive Maintenance
Connected vehicles track health in real-time and provide early warnings to the driver instead of waiting until something is wrong.
- Traffic Efficiency and Smart Cities
Connected vehicles minimize congestion and travel time because they provide data to traffic systems.
Applications of Connected Vehicles
- Navigating and Traffic Control in Real-Time
Smart cars offer proper navigation with real-time traffic information and save on time and stress.
- Emergency Assistance/Crash Notification
Connected cars are able to automatically call emergency services in case of an accident.
- Remote Vehicle Monitoring and Control
Mobile applications allow drivers to lock and unlock their cars, as well as monitor them remotely.
- Freight Management and Logistics
Connected vehicles allow fleet operators to optimize routes, track driver behavior, and improve cost-effectiveness.
- Telematically-Based Insurance and Telematics
The insurance companies use the data of vehicles to provide personalized premiums.
Connected Vehicles and Autonomous Vehicle Technology
Connected vehicles represent a very important phase to complete autonomous vehicle technology. Connectivity gives autonomous systems access to external information that sensors do not have the capacity to record.
Through communication with infrastructure and other cars, autonomous systems have a better insight into the surrounding world, which enhances decision-making and safety.
The Data and AI role in connected car technology
Connected vehicles are driven by data. AI converts raw data into actionable insights, which will give smarter mobility solutions.
Connected cars, Cybersecurity, and Privacy
Cybersecurity is becoming necessary as vehicles get interconnected. Manufacturers and regulators put data and systems protection as a top priority.
Smart City Ecosystems Connected Vehicles
Connected vehicles are part of smart cities, which allows smart traffic control and mobility that is also sustainable.
Difficulties in Connected Vehicles Adoption
In spite of the advantages, there are still challenges of infrastructure preparation, expenses, and standardization.
Connected Vehicle Technology: Future Trends
The future of connected cars will be determined by the development of 5G, edge computing, and software-defined vehicles.
Effects of Connected Vehicles in the Auto Industry
New opportunities are available in the industry since mechanical engineering is giving way to software-driven innovation.
In connected vehicles, the Future Road Ahead: Research and Innovation
There is a possibility of full utilization of connected vehicle technology through continuous research and development. Automobile research and development centers are significant in supporting connectivity, safety, and sustainability.
The Suzuki R&D Center India and other organizations are also taking this change by considering the next-generation mobility solutions towards serving different markets. These types of research focus help to produce a safer, smarter, and more connected future of mobility using connected car technology and smart systems.
Conclusion
Connected vehicle technology is transforming how we drive, interact with our cars, and experience mobility. From safety and efficiency to sustainability and automation, connected vehicles are laying the foundation for the future of transportation. As technology continues to evolve, connected vehicles will become an integral part of everyday life, seamlessly blending digital intelligence with human mobility.
FAQs
- What is a connected vehicle in simple terms?
A connected vehicle is a car that uses internet connectivity to communicate with other vehicles, infrastructure, and cloud services. - Are connected vehicles the same as autonomous vehicles?
No, but they are closely related. Connected vehicles support autonomous vehicle technology by providing real-time data. - What are the main benefits of connected vehicle technology?
Improved safety, better traffic management, predictive maintenance, and enhanced driving experience. - Do connected vehicles require constant internet access?
Most features rely on connectivity, but essential driving functions work independently. - Are connected vehicles secure?
Manufacturers implement advanced cybersecurity measures to protect vehicle systems and user data.