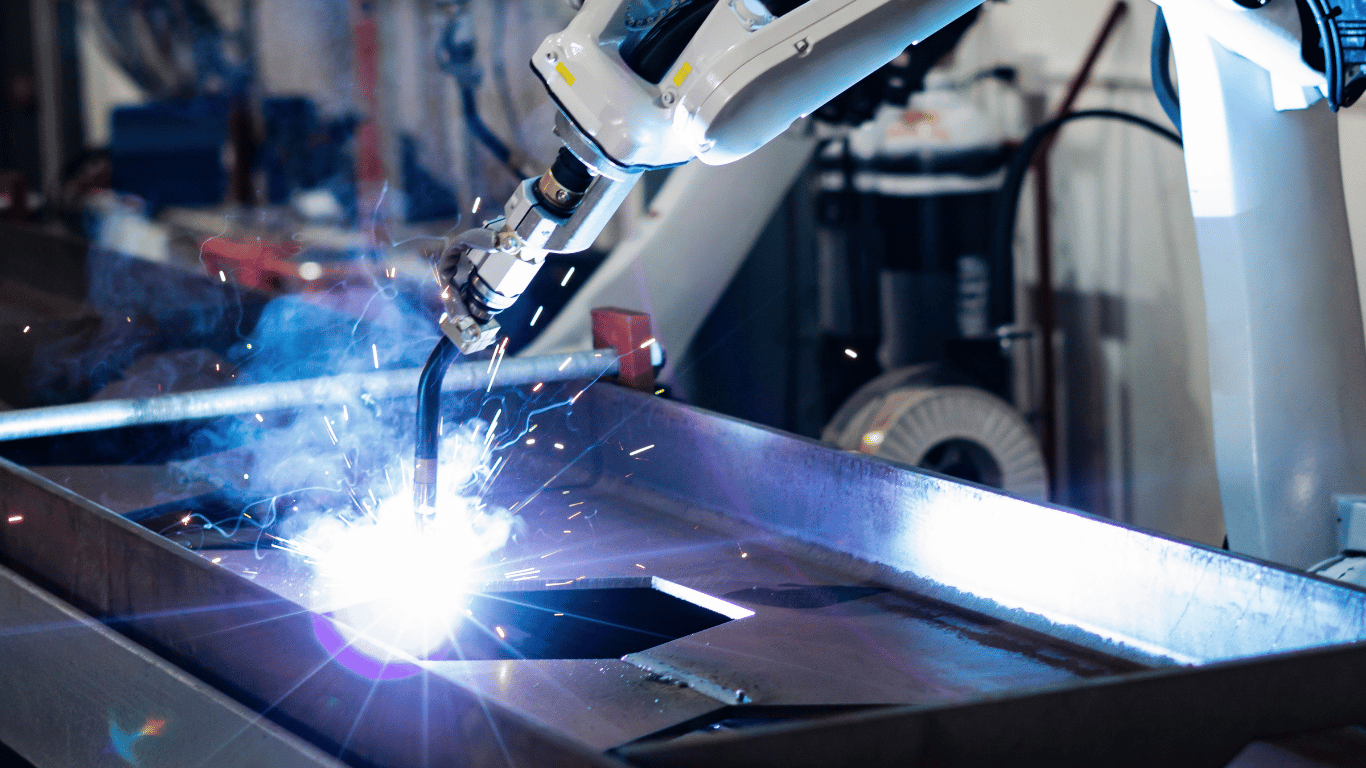
Beyond the Human Hand: An In-depth Look at the Global Robotic Welding Market
The global robotic welding market is at the forefront of the modern manufacturing revolution, representing a powerful shift from manual labor to automated precision. Robotic welding systems, which include robotic arms, controllers, vision systems, and specialized welding equipment, are transforming industries by offering unparalleled levels of consistency, speed, and safety. This technology is no longer a luxury reserved for large-scale operations; it is becoming an accessible and necessary tool for manufacturers of all sizes who are looking to enhance productivity, overcome labor shortages, and maintain a competitive edge.
The global robotic welding market size reached nearly USD 4501.10 Million in 2024. The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.00% between 2025 and 2034, reaching around USD 9717.54 Million by 2034. This robust growth trajectory underscores the profound impact of automation on industrial processes and a global commitment to improving efficiency and quality in manufacturing.
The Driving Forces Behind Market Growth
Several key factors are propelling the robotic welding market forward:
- Addressing the Skilled Labor Shortage: A critical challenge facing the manufacturing sector worldwide is a severe shortage of skilled welders. Manual welding is a physically demanding and highly specialized trade, and a significant portion of the workforce is nearing retirement. Robotic welding provides a scalable and reliable solution to this problem, allowing companies to maintain and even increase production without being constrained by labor availability.
- Improving Productivity and Efficiency: Robotic welding systems can operate continuously with minimal downtime, significantly increasing a production line’s output. They perform welds with a high degree of speed, repeatability, and precision, eliminating human error and leading to a more consistent and higher-quality final product. This enhanced efficiency directly translates to cost savings and a faster time to market.
- Enhancing Worker Safety: The welding process exposes workers to significant health and safety risks, including toxic fumes, intense heat, and UV radiation. By automating the welding process, companies can remove human workers from these dangerous environments, drastically reducing the risk of injury and long-term health issues. This focus on worker well-being is a major driver of investment in robotic solutions.
- Advancements in Technology: The continuous evolution of robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine vision systems is making robotic welding more versatile and accessible. AI-powered systems can now “learn” and adapt to new welding tasks, while advanced vision systems can detect imperfections and adjust the welding path in real-time, even on complex geometries. These technological leaps are expanding the range of applications for robotic welding, from small-scale fabrication to large-scale construction.
- Growth in Key End-User Industries: The demand for robotic welding is directly linked to the health of key industrial sectors. The automotive industry, in particular, is a major consumer, leveraging robotic welding for high-volume production lines. The aerospace, construction, and heavy equipment industries are also significant drivers of growth, as they increasingly adopt automation to improve precision, quality, and speed in complex fabrication tasks.
Market Segmentation and Key Trends
The robotic welding market is highly segmented, reflecting a diverse range of applications and technological solutions.
- By Robot Type: The market is primarily divided into traditional articulated robots and emerging collaborative robots (cobots). Articulated robots, which are typically larger and enclosed for safety, dominate high-volume, repetitive tasks. Cobots, which are smaller, more flexible, and can work alongside human operators without a safety cage, are a fast-growing segment, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and for low-volume, high-mix applications.
- By Welding Process: The most common applications are arc welding (including MIG/MAG, TIG, and submerged arc welding) and spot welding. Spot welding holds a large market share, particularly in the automotive industry. However, the use of robotic arc welding is growing rapidly across various sectors due to its versatility and ability to handle a wide range of materials.
- By End-User Industry: The automotive and transportation sector is the largest end-user. However, other industries like heavy machinery, construction, aerospace, and energy are all significant and growing consumers of robotic welding technology. The adoption of robotic welding in these sectors is driven by the need for high-strength, precise welds that meet strict regulatory and safety standards.
Competitive Landscape and Challenges
The global robotic welding market is dominated by a few major players, including ABB, Fanuc, Kuka, and Yaskawa Electric. These companies are global leaders in robotics and have strong brand recognition, extensive R&D capabilities, and vast global distribution networks. They compete on a variety of factors, including system performance, ease of use, and comprehensive after-sales support. However, a growing number of smaller, more agile companies and system integrators are entering the market, often specializing in specific applications or offering more cost-effective solutions.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces a few key challenges. The high initial investment cost for a robotic welding system can be a barrier for smaller companies. Additionally, the complexity of programming and operating some systems requires a skilled workforce, which can be a hurdle to adoption. Finally, a significant challenge is the need to integrate these new systems into existing production lines without causing major disruptions, which often requires significant planning and custom engineering.
The Future of the Market
The projected growth to around USD 9717.54 Million by 2034 paints a clear picture of an exciting and transformative future. The market will be defined by a continued focus on democratizing access to automation, with more user-friendly interfaces and more affordable cobots. The integration of AI and machine learning will become more sophisticated, enabling robots to handle even more complex and varied welding tasks, from one-off bespoke jobs to mass production.
Furthermore, the industry will see a greater emphasis on cloud connectivity and data analytics, allowing manufacturers to monitor and optimize their welding operations in real-time, predict maintenance needs, and ensure quality control across multiple sites. The global push for more sustainable and efficient manufacturing will also drive demand for robots that can work with new, lightweight materials. The robotic welding market is well-positioned to remain a cornerstone of modern industry, providing the precision, safety, and productivity needed to build the world of tomorrow.