Understanding DVT Symptoms: Early Signs, Risks, and Prevention
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. These clots can cause serious complications if they break loose and travel to the lungs, leading to a life-threatening pulmonary embolism. Identifying DVT symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
Common DVT Symptoms
Recognizing DVT symptoms at an early stage can help prevent severe complications. Some of the key signs to watch out for include:
1. Swelling in the Affected Leg
One of the most noticeable DVT symptoms is swelling, usually in one leg. The affected limb may appear larger than the other, and the swelling might worsen over time.
2. Leg Pain or Tenderness
Pain in the calf or thigh is another common symptom. The discomfort might start as mild but can become severe over time, especially when standing or walking.
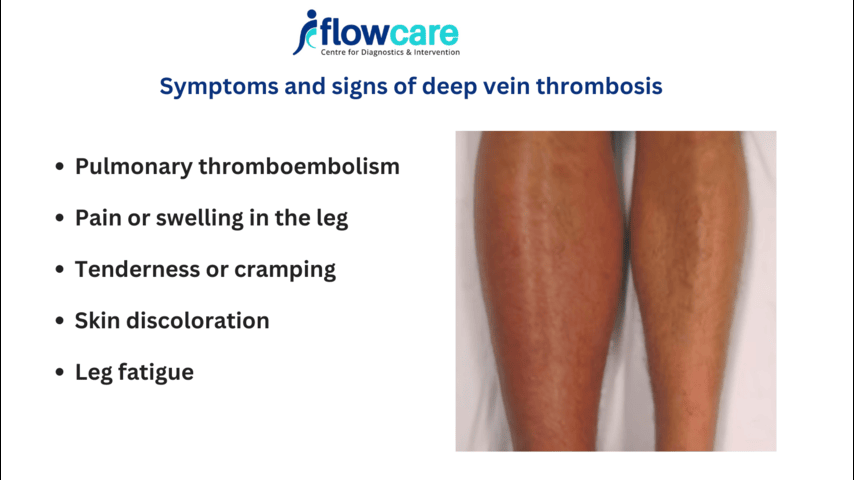
3. Skin Discoloration
A reddish or bluish tint on the skin of the affected leg may indicate poor blood circulation due to a clot. The skin might also feel warm to the touch.
4. Warmth Over the Affected Area
The skin surrounding the clot may feel warmer than the surrounding areas, signaling inflammation caused by the clot.
5. Visible Veins
In some cases, veins may appear more prominent due to the blockage of blood flow, making them more visible on the skin.
6. Cramping or Aching
Some people experience a cramping sensation, similar to a pulled muscle, but it persists and worsens over time.
Risk Factors for DVT
While DVT can affect anyone, certain factors increase the risk of developing a blood clot. These include:
- Prolonged Immobility: Sitting for long periods, such as during long-haul flights or bed rest, can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Surgery or Injury: Recent surgery, particularly involving the legs or abdomen, can make clot formation more likely.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased pressure on veins during pregnancy can contribute to clot development.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional strain on veins, leading to poor circulation.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases clotting tendencies.
- Family History: A genetic predisposition to clotting disorders can make DVT more likely.
- Hormonal Medications: Birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy can increase the risk of clot formation.
How is DVT Diagnosed?
If you experience DVT symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. Doctors use various tests to diagnose DVT, including:
- Ultrasound: The most common test, which uses sound waves to detect blood clots in veins.
- D-dimer Test: Measures a substance released when a blood clot dissolves. High levels suggest possible DVT.
- Venography: A special X-ray test where contrast dye is injected into a vein to detect clots.
- MRI or CT Scan: In complex cases, advanced imaging helps locate deep clots.
Treatment Options for DVT
Early treatment is essential to prevent complications. The most common treatment options include:
1. Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants)
Medications like heparin and warfarin help prevent new clots from forming while the body dissolves existing ones.
2. Compression Stockings
These special stockings improve blood flow in the legs and reduce swelling and discomfort.
3. Thrombolytic Therapy
In severe cases, clot-dissolving drugs may be used to break down large clots quickly.
4. Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter
For patients who cannot take blood thinners, a filter may be placed in the vena cava to prevent clots from reaching the lungs.
Preventing DVT
While medical treatment is available, prevention is always the best approach. Here are some ways to lower your risk:
- Stay Active: Avoid prolonged sitting or standing. If you work at a desk, take short breaks to walk around.
- Wear Compression Stockings: These help improve blood circulation, especially during long flights or post-surgery recovery.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration keeps blood from thickening, reducing clot risk.
- Exercise Regularly: Activities like walking, swimming, or stretching promote healthy circulation.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess weight reduces strain on veins.
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Both can contribute to blood clotting disorders.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you experience any DVT symptoms, such as persistent swelling, leg pain, or difficulty breathing, seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent life-threatening complications.
Conclusion
Deep Vein Thrombosis is a serious condition that requires prompt attention. Recognizing DVT symptoms and understanding risk factors can help prevent complications. By maintaining an active lifestyle, staying hydrated, and seeking medical advice when needed, you can significantly lower your risk. If you suspect DVT, consult a healthcare professional immediately for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.








Post Comment